Solve Pest Problems
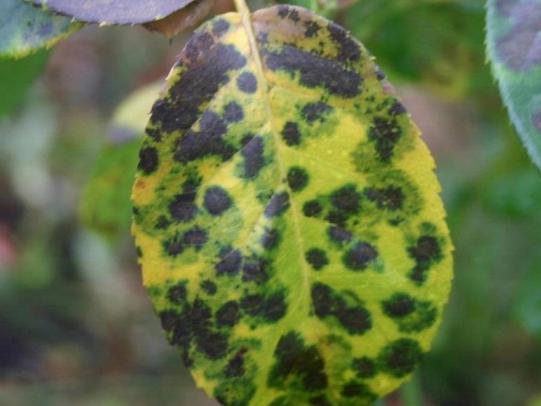
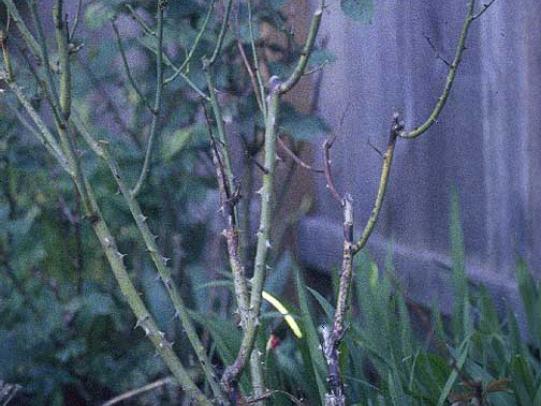
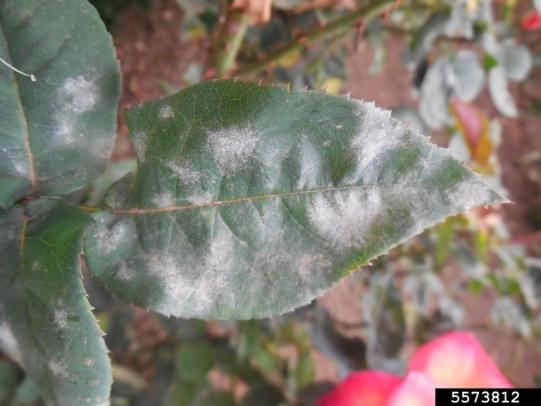
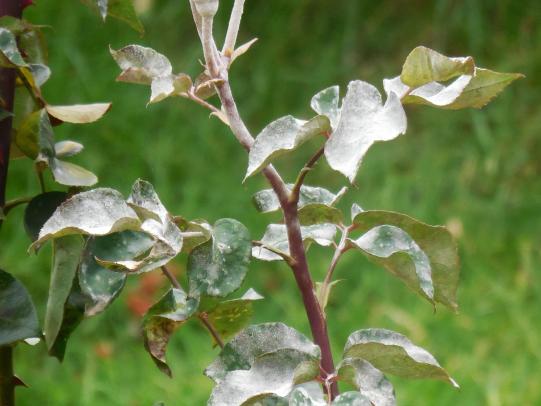
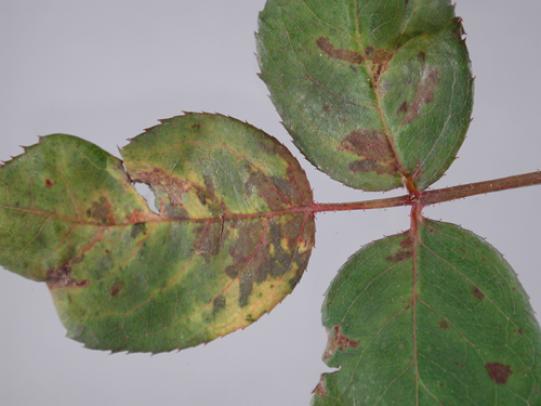
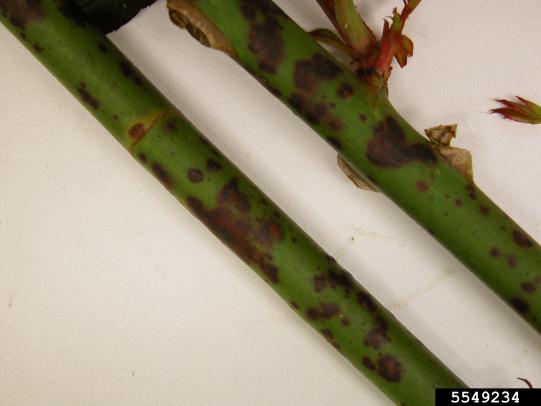
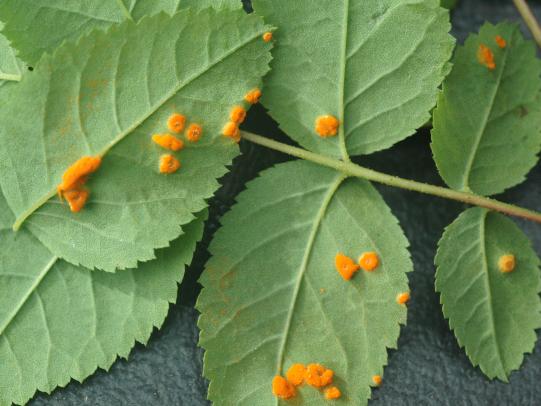
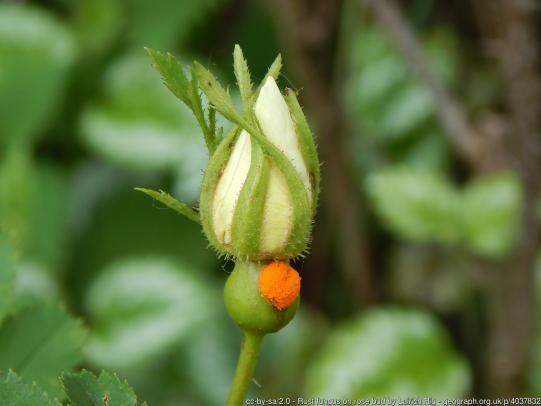
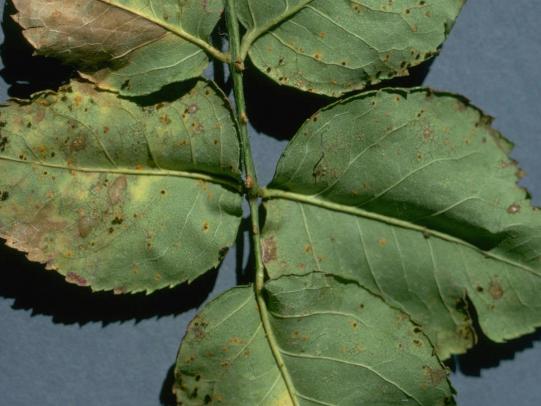
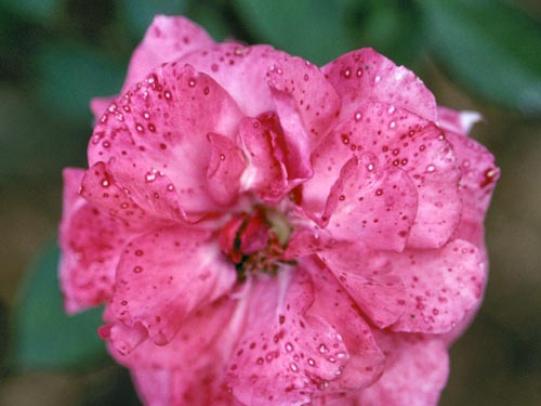
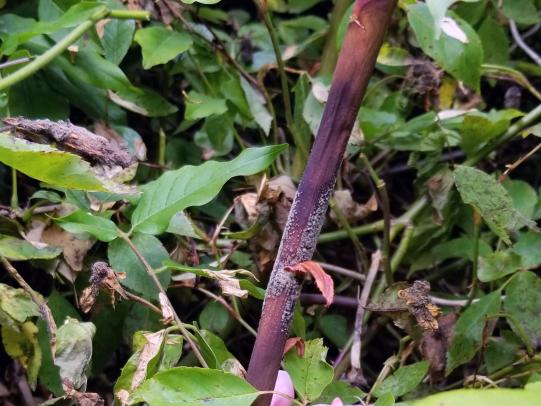
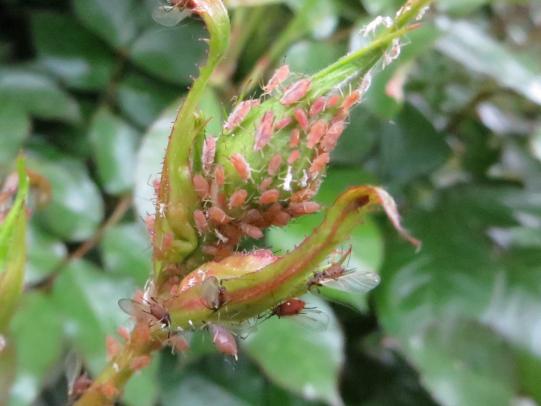
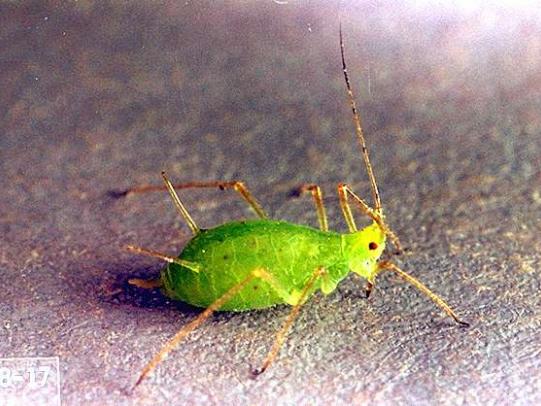
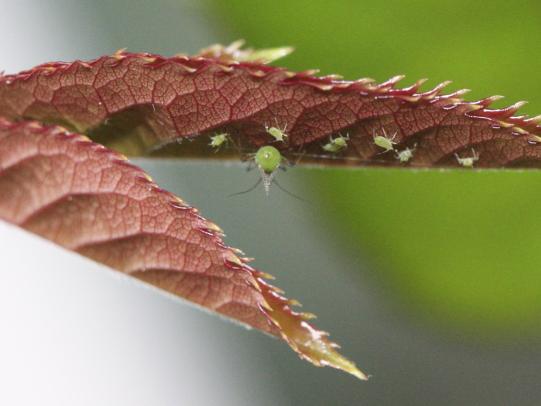
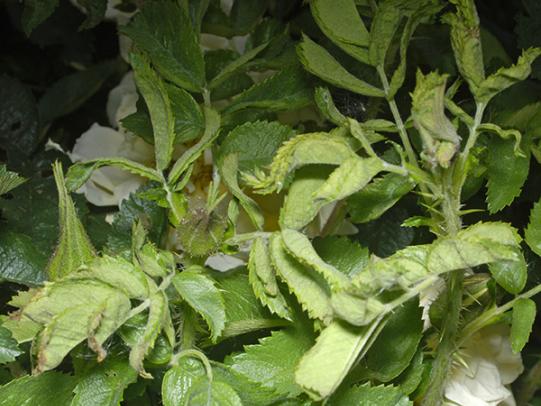
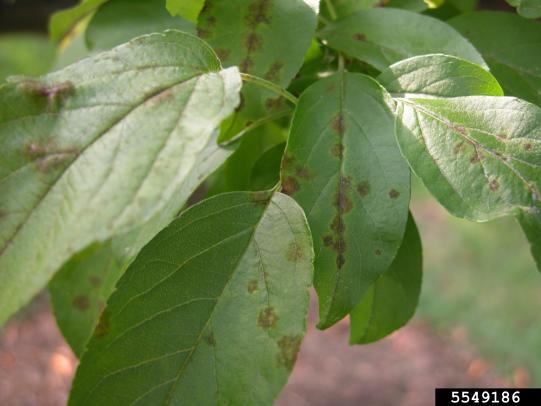
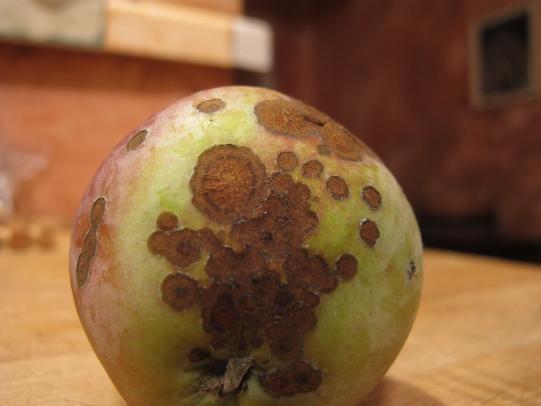
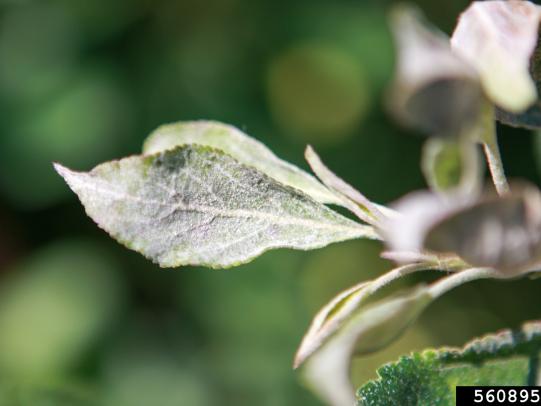
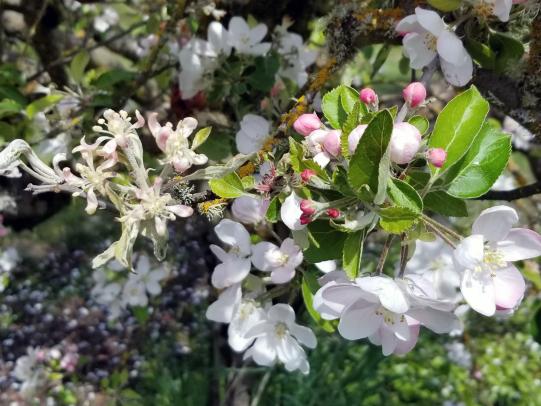
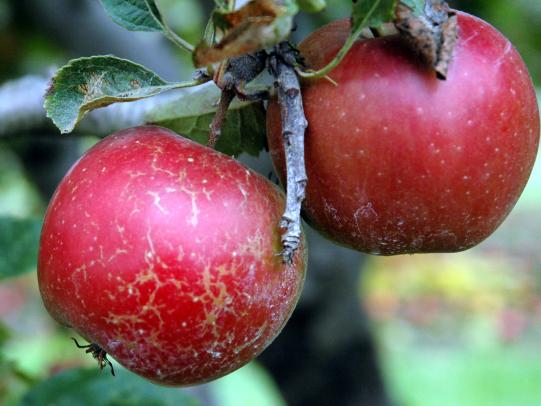
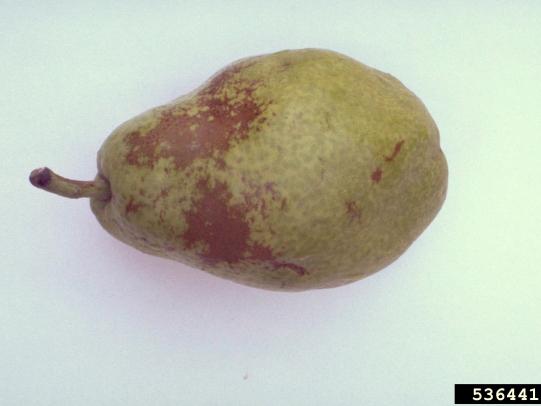
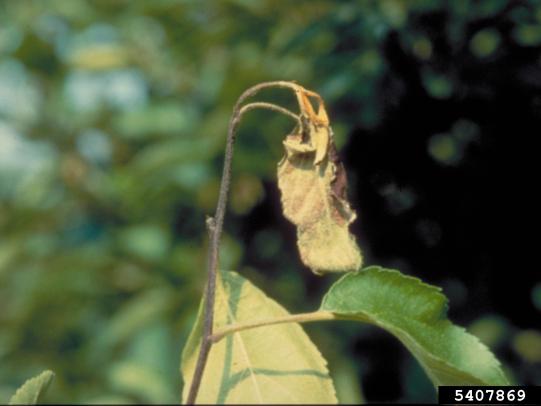
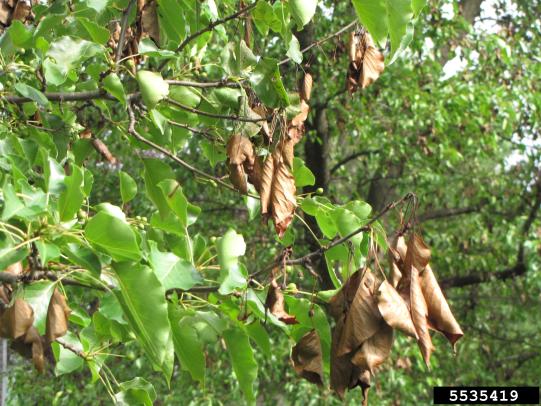
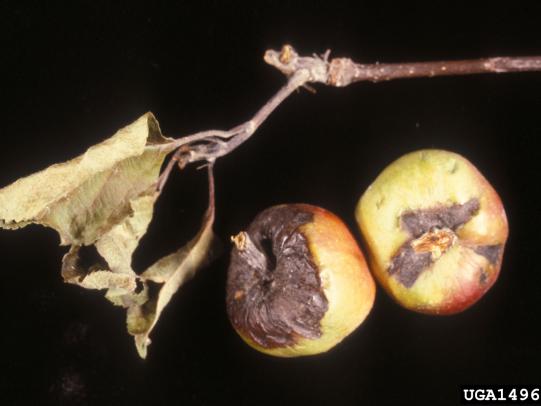
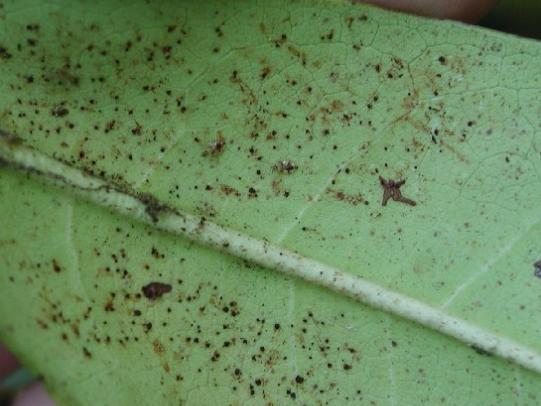
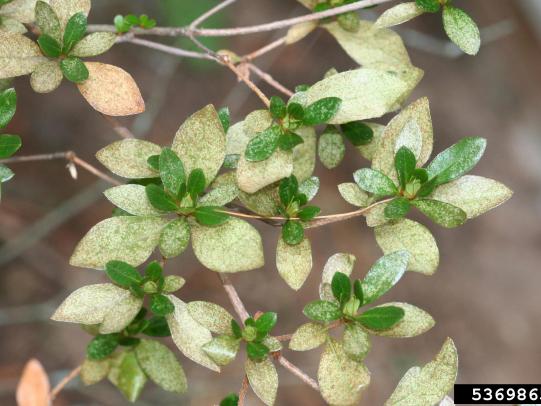
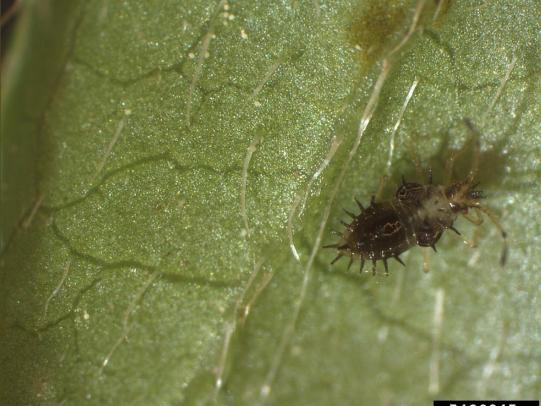
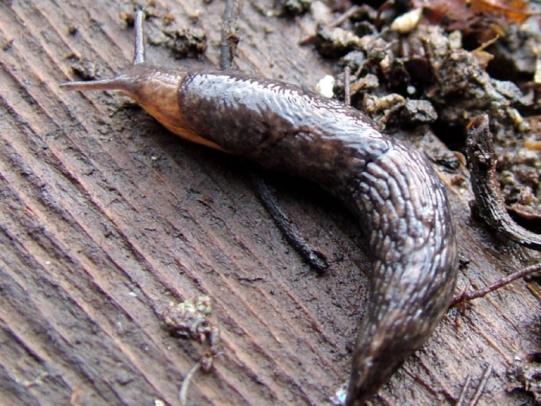
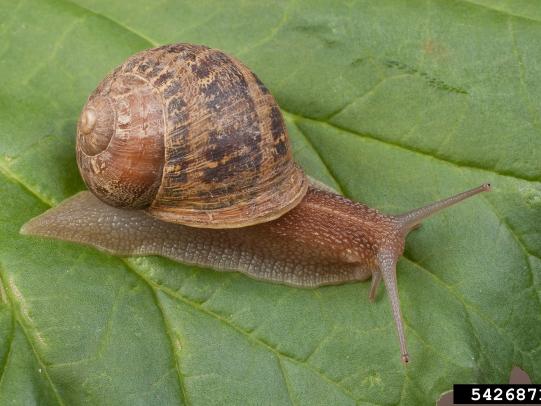
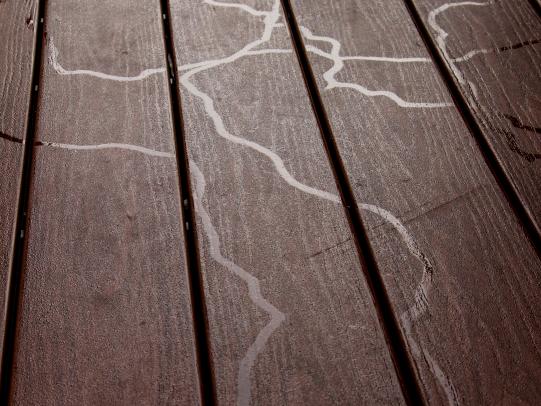
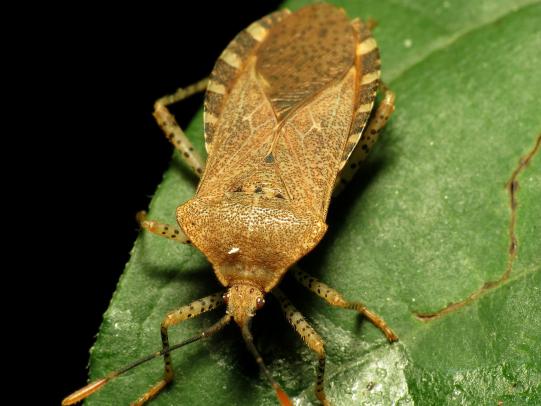
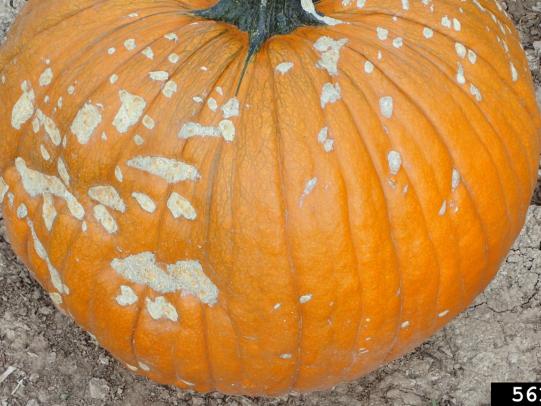
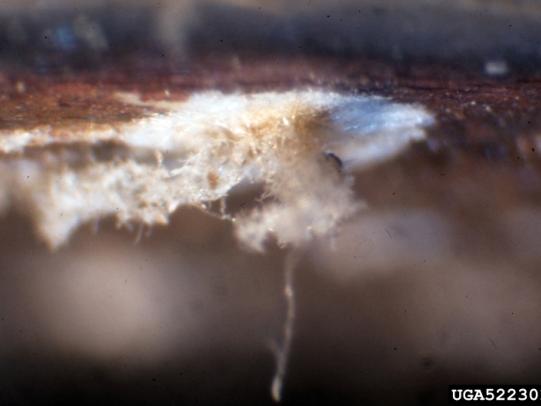
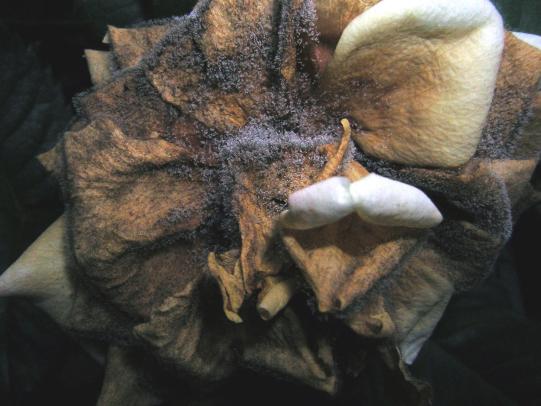
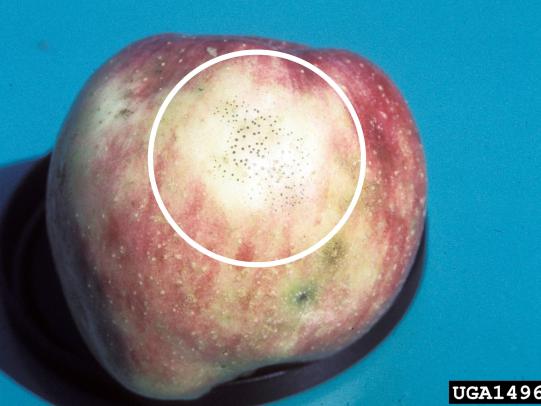
Many dozens of plants grow in Oregon gardens and landscapes. Each plant type has many common insect pests, plant diseases, and cultural (non-living) problems. Some common plant pests are shown below as examples.
We are continuing to build more pages as our funding allows. Please consider making a donation to this effort!